This is an old revision of the document!
LESSON 14: Using "For" to make successive calculations
In this lesson we will calculate the biomass of the expanded Legal Amazon Protected Areas per year. For this, we will use:
- The protected areas map in the year 2000
Guidebook_Dinamica_5/Database/Protected_areas/protected_areas_2000.tif - The protected areas map in the year 2006
Guidebook_Dinamica_5/Database/Protected_areas/protected_areas_2006.tif - The Legal Amazon Biomass map
Guidebook_Dinamica_5/Database/biomass/biomass.tif
Initially, we need to open all files that will be used. Grab two Load Categorical Map functors and place them on the sketch. Double click each Load Categorical Map and open the protected areas map files for 2000 and 2006. Also grab and place one Load Map and open the Legal Amazon Biomass map.
Grab and place on the sketch one Calculate Map. Click on the hook tool to insert three Number Maps. Assign a number to each Number Value. Connect the Load Map and Load Categorical Map to the Number Map functors.
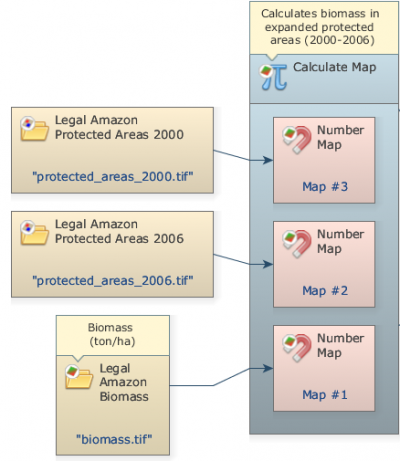
Now, write the following code inside the Calculate Map to calculate the biomass in protected areas designated between 2000 and 2006 using the Number Map functors:
if not isNull(i2) and isNull(i3) then
i1
else
null

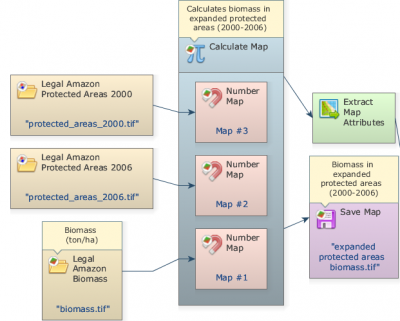
Select the IEEE 754 32 bit real as the data cell type. Grab and place on the sketch a Save map and connect Calculate Map to it. Open Save Map, browse to Guidebook_Dinamica_5/Models/Set_3/basics/3_calculate map4/ and chose a file name (e.g. expanded protected areas biomass.tif).
Grab and place on the sketch Extract map attributes and connect Calculate Map to it.
Now, grab and place on the sketch one Calculate value functor. Click in the hook tool to create three hooks inside the Calculate Map: one Number table and two Number value hooks. Click on the Number value functor and number table with the Functor Editor tool and enter “1”, “2” and “3”, respectively. This is a number identifier for each element and will be represented within the equation box as v1 (value 1), v2 (value 2) and t1(table 1) respectively.
Grab and place on the sketch two Real value functors to insert a double precision real constant: A CO2 conversion factor (3.666) and a Carbon Content (0.47). Connect the Extract map attributes Map to Number Table and the two Real Value functors to Number Value Functor inside the Calculate Value.
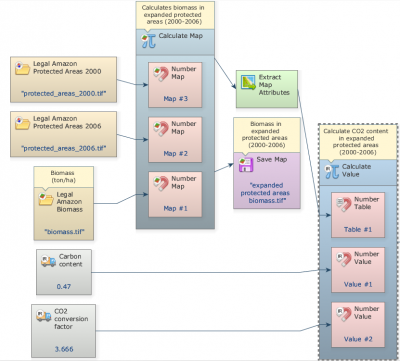
Now, write the following equation inside the Calculate Map to calculate CO2 content in the created protected areas between 2000 and 2006:
t1[“cellSum”] * t1[“cellArea”] * v1 * v2
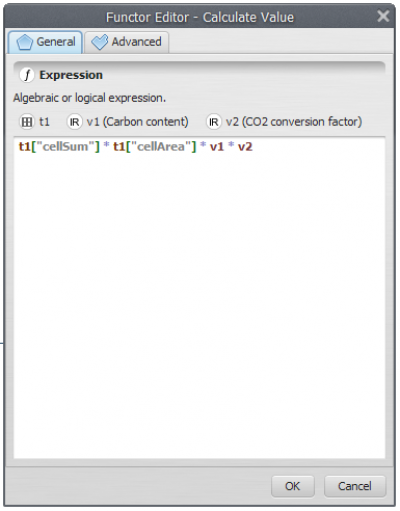
Grab and place on the sketch one Set Lookup Table Value Functor to insert the calculate values into a lookup table. It is important to pay attention to add correctly the key to the line in which the value will be inserted.
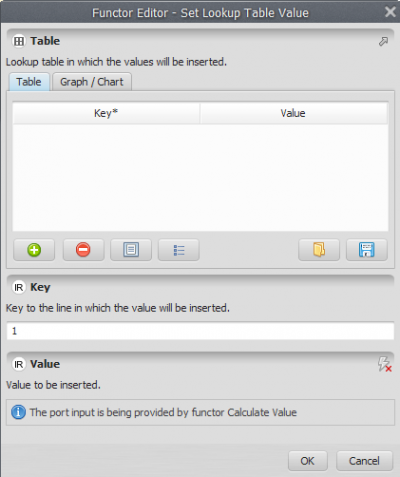
Click on the Input/output from the library window, grab and place on the sketch the Save Lookup Table functor. Connect the Set Lookup Table Value to Save Lookup Table. Open Save Table, browse to the ''Guidebook_Dinamica_5/Models/Set_3/basics/3_calculate map4/ and write the name file (expanded protected areas co2.csv).
Mark the eye button at the top of “Save Table” to view the results after model is run. Save and run the model!
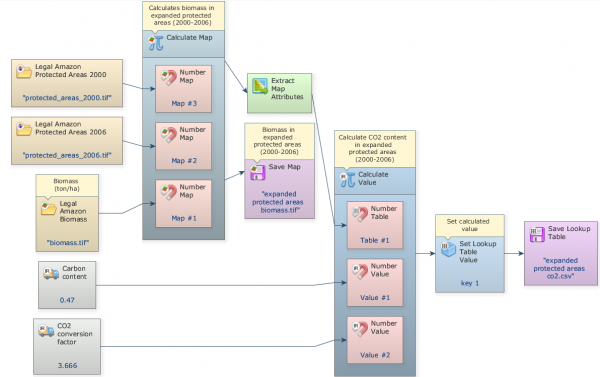
Click on the layout tool Left to Right and your final model will look like the one below:
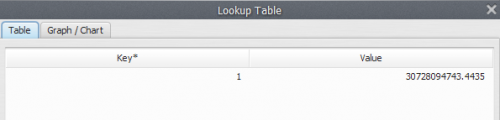
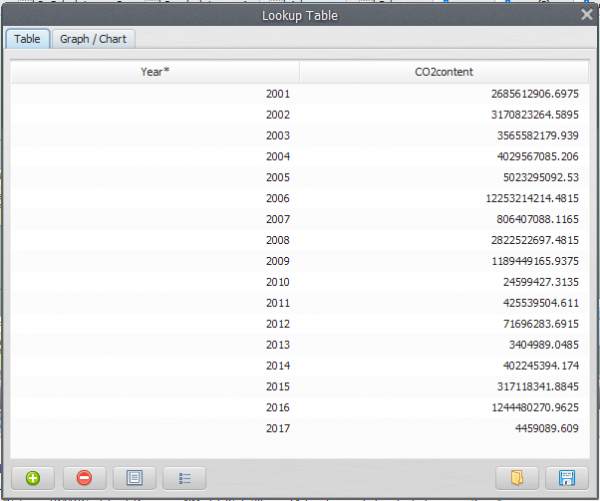
Now, click on eye button of “Save Lookup Table” to see the result. This functor output is a table that looks like this:
Now, a different map is produced for each iteration, calculating a map containing the remaining forest for each category.
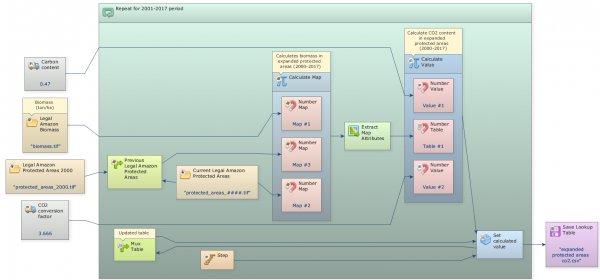
Grab the container Repeat from the Control tab and place it on the sketch. Drag the previously model into it. It will automatically resize to envelop Calculate Map.
Then add the functor Step into Repeat. Open Calculate Map by clicking on its top left icon and connect Step to Value port of Number Value. The Step functor self-associates to the enveloping container and passes to Calculate Map the current step. Thus for each iteration Calculate Map produces a map containing the current Amazon Protected areas for each time step.
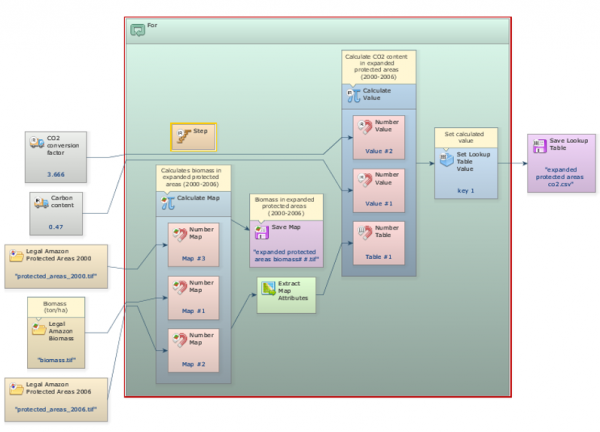
Now you need to fill in a table in order to store the area calculated for each category. The functor Set Table Cell Value updates a table placing a value to a position defined by a key. To fill in the entire table, you need to develop a iteration that enables this functor to browse through the table. To close the loop, you will the mux functors.
A Mux functor can be a map, a categorical map, a lookup table, a table or a value. Find in the Control tab Mux Table and drag it into Repeat. Also drag Set Table Cell Value from the Table tab.
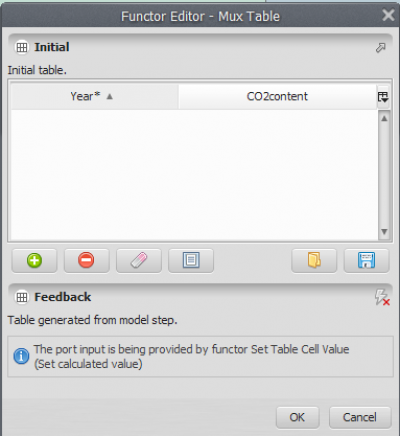
Now, click on the Mux Table with the Edit Functor Ports. Every Mux functor has two input ports. In the first iteration, it reads the input from the Initial port; thereafter it receives the data from the model step through the port Feedback. This process allows data to be updated in the model, thus becoming dynamic. Hence this functor is key to the incorporation of feedback into a dynamic model.
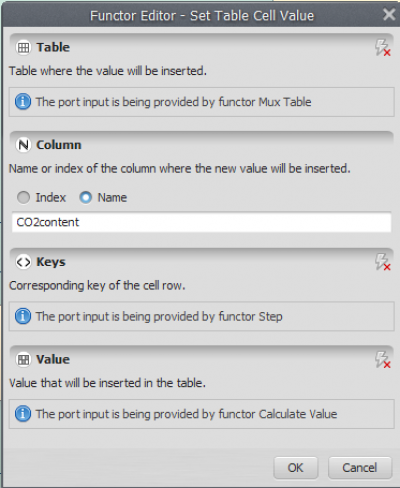
Also open Set Table Cell Value with the Edit Functor Ports. This functor receives a table that will be updated with a value placed in a position defined by a key. You need to connect table output from the functor Mux Lookup table to the input port of Set Table Cell Value.
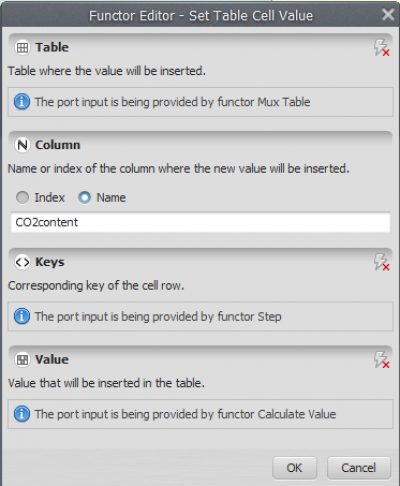
Again, let’s connect the output from Set Table Cell Value to Mux Table. When a connection has two or more options, the Edit Functor Ports window opens automatically. You have to choose the port Feedback.
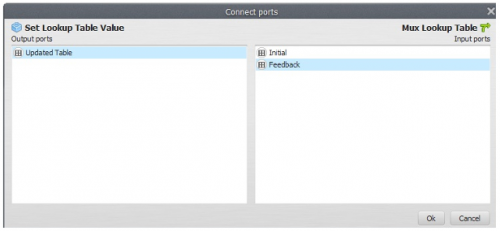
Now click on the port Initial with the right mouse button. You will open a table editor. In this case you just need to enter “0“ and “0” as Key and Value for the first table record, and then save these inputs using the ”+” button.
Still, you need to connect the output from Calculate Value to the input port of Set Lookup Table Value.
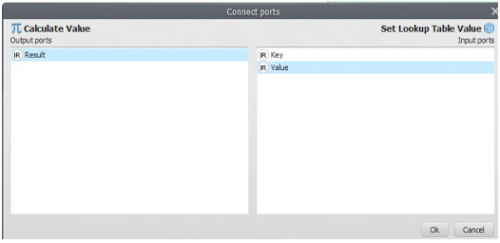
The Edit Functor Ports window pops up because there are two options. Connect the arrow to the port Value; the key comes from the current model step via the connection of Step to Set Lookup Table Value.
Observe that the feedback connection is between Mux Lookup Table and Set Calculate Value. As a last step, you need to save the lookup table into a file. Drag the functor Save Lookup Table from the Input/Output tab. Connect Set Lookup Table Value to it and edit the name for the CSV file.
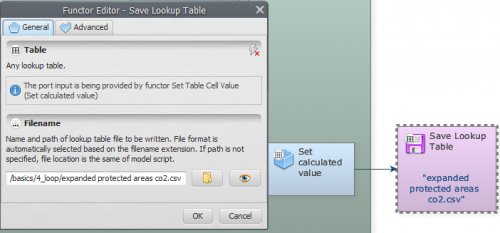
As a last step, you need to save the lookup table into a file. Drag the functor Save Lookup Table from the Input/Output tab. Connect Set Lookup Table Value to it and edit the name for the CSV file.
Mark the eye button at the top of “Save Table” to view the results.
Save and run the model!
Click on the layout tool Left to Right and your final model will look like the one below:
Now, click on eye button of “Save Lookup Table” to see the result. This functor output is a table that looks like this:
Congratulations, you have successfully completed this lesson! Now let’s move to the next lesson: LESSON 15: Using "while" to make successive calculations
